Multiple Choice
Identify the choice
that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
Due
to gravity the Moon orbits the Earth. If somehow the gravitation force from these two celestial
objects was removed, what would happen to the Moon?
a. | The Moon would continue to revolve around the Earth, but its speed would be
slower | b. | The Moon would fly off into space in a straight line away from the
Earth | c. | Both celestial objects would immediately fall into the Sun and be
destroyed. |
|
|
|
2.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
What motion do all three
of the celestial objects shown above have in common?
a. | They all spin due to the force of electromagnetism | b. | They all move
diagonally across the solar system. | c. | They all rotate due to the force of
gravity |
|
|
|
3.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
Saturn’s Rings | 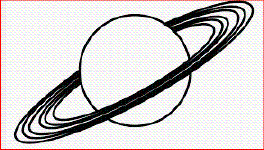 Saturn Saturn | |
Look at the diagram of Saturn displayed above. Note that Saturn has
rings around it. These rings are made of small rocks, ice, and cosmic dust that are held in place by
gravity. Identify the motion of these rings.
a. | This planet’s rings are moving upward and downwards due to the solar wind.
| b. | These rings do not have any motion. They are static. | c. | The rings are
orbiting (revolution) around Saturn due to gravity. |
|
|
|
4.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity and Celestial
Motion)
Which of these has the greatest effect on the motion of planets in the solar
system?
a. | electromagnetic
forces | b. | gravitational forces | c. | frictional
forces |
|
|
|
5.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
Examine the picture shown above. Notice that it is showing the orbital
path of the Moon as it moves around the Earth.. Identify this motion
a. | The Moon’s motion in this example is called rotation. | b. | This motion is
called revolution | c. | The diagram above is showing how the Moon spins
around the Earth. |
|
|
|
6.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity and Celestial
Motion)
Which keeps Earth in its orbit?
a. | the gravity of the sun | b. | the rotation of Earth | c. | the revolution of
the moon |
|
|
|
7.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
Look
at the graphic shown above. Notice the arrows and letters (A, B, and C) next to the arrows.
Identify the celestial phenomena being illustrated by each arrow.
a. | A=Gravitational pull, B=Rotation,
C=Revolution | b. | A=Magnetic force, B=Rotation,
C=Revolution | c. | A=Gravitational pull, B=Solar wind,
C=Revolution |
|
|
|
8.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity and Celestial
motion)
Which of these keeps a moon in orbit around a planet?
a. | composition | b. | gravity | c. | shape |
|
|
|
9.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
A student drew a
diagram of Earth at four different points in its orbit around the sun. The student drew arrows to
represent the direction of the gravitational force of the sun on Earth.
Which arrow did the student draw incorrectly?
a. | Arrow 4 | b. | Arrow 2 | c. | Arrow
3 |
|
|
|
10.
|
SPI 0807.12.6 (Gravity-Celestial
Motion)
Which of these is
most directly affected by gravity?
a. | the magnetic field
surrounding Earth | b. | the orbit of the moon around Earth | c. | the rotation of Earth on its
axis |
|