|
|
|
1.
|
Stnd 03: Kinematics A car traveling to the West begins to slow down
as it approaches a traffic light.
Which statement concerning the motion of the car is
correct?
a. | The car’s acceleration is positive. but the velocity is
negative | b. | The acceleration of the car is negative, but the velocity is
positive. | c. | The car’s acceleration is positive. The cars velocity is also
positive. | d. | The car’s acceleration is negative. The car’s velocity is also
negative. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Stnd 03: Kinematics A basketball player shoots a free-throw. The
motion of the basketball is shown below. Describe the motion of the
basketball after it leaves the player’s hands, and explain how this is an example of
acceleration.
a. | The ball travels in curved trajectory in a single direction with decreasing speed.
This is acceleration because of the change in velocity. | b. | The ball moves
downwards and then upwards in an arc. This is acceleration because of the change in force pulling the
ball downwards. | c. | The ball travels in a horizontal line to the basket with increasing speed. This is
acceleration because of the change in velocity. | d. | The ball travels in a curved trajectory in two
directions with decreasing speed. This is acceleration because of the change in direction.
|
|
|
|
3.
|
Stnd 03: Kinematics In 1969 astronauts first traveled to the Moon in
the Saturn-5/Apollo spacecraft. Lunar
Module | Saturn V-Apollo Spacecraft | Command Module | | | | | | |
This rocket ship blasted off from the launch pad
in Florida and was propelled with ever increasing speed upwards through the Earth’s atmosphere
flying towards the Moon.
Which one of the following graphs best represent the motion of
this rocket ship after it blasted off from the launch pad?
|
|
|
4.
|
Stnd 04: 2nd Law of Motion
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states
that force is equal to mass times acceleration.
If the force acting on the object stays the
same but the mass increases, what is most likely to happen to the acceleration of the
object?
a. | Velocity will change but the speed and direction will remain
constant. | b. | Acceleration will increase | c. | Acceleration will decrease | d. | Acceleration will
stay the same |
|
|
|
5.
|
Stnd 04: 2nd Law of Motion
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is
9.8 ,/s2. The force acting on an object on Earth is 16 Newtons.
What is the mass of
this object on Earth?
a. | The mass is .6125 kilograms | b. | The object’s mass is 156.8
kilograms | c. | Mass of the object is 1.63 kilograms | d. | Mass of the object is 2.6
kilograms |
|
|
|
6.
|
Stnd 04: 2nd Law of Motion
A small car and big truck are driving down
a two-lane highway on a rainy day. The car is in the left lane, and the truck is in the right lane.
Both vehicles are traveling North at the same speed (70 MPH). Both drivers see a traffic jam up
ahead, and they both slam on theirs brakes with all of their might at the same moment. The car comes
to a halt after traveling 30 feet. The truck, however, does not halt until 120 feet.
Why does
it take the truck longer to come to a complete stop even though both vehicles were moving at the same
speed?
a. | Because both cars were maintaining the same constant velocity. | b. | Because vector
quantities and scalar quantities are not the same thing | c. | The mass of the car
is much greater than the mass of the truck. | d. | The mass of the truck is much greater than the
mass of the car. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Stnd 05: 3rd Law of Motion
The diagram below shows a 5.00 kg block at
rest on a horizontal, frictionless table. Gravity is acting on this block, and the acceleration of
gravity on Earth is 9.807 m/s 2. Which of the following diagrams
best represents the force exerted on the block by the table?
|
|
|
8.
|
Stnd 05: 3rd Law of Motion
A man is pushing a wheelbarrow full of dirt
as he works on a project in his back yard. Compared to the magnitude of the force exerted
on the wheelbarrow by the man, the magnitude of the force exerted on the man by the wheelbarrow
is...?
a. | zero | c. | somewhat smaller | b. | the same | d. | larger |
|
|
|
9.
|
Stnd 05: 3rd Law of Motion
The magnitude of the force that a baseball
bat exerts on a ball is 50 Newtons The magnitude of the force that
the ball exerts on the bat is...?
a. | 10 N | b. | 250 N | c. | 50 N | d. | 5.0 N |
|
|
|
10.
|
Stnd 05: 3rd Law of Motion
Both dogs in the picture below have the
same mass, and they both are exerting the same amount of force on the rope toy, What is most likely to happen when the rope
toy breaks in the middle as a result of the forces the dogs are exerting?
a. | The dogs will be thrown backwards, in opposite directions from each other, the same
distance. | b. | The breaking of the rope toy will create unbalanced forces that only affect one of
the dogs, causing one dog to be thrown backwards. | c. | As the two dogs are the same mass, neither dog
will be thrown backwards. | d. | One dog will be thrown backwards while the
other dog will be able to move forwards. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Stnd 06: Properties of Waves
To play high pitch notes on a guitar, a
musician must decrease the length of the strings by pressing down on the strings with his or her
fingers as they are being plucked or strummed. Now
imagine that a guitar string is cut into four pieces of different lengths as shown below. Each
piece is stretched between two supports to the same tightness.
If each piece was plucked in
the middle with the exact same amount of force, which of the pieces would have the highest number of
wave oscillations during one second?
|
|
|
12.
|
Stnd 06: Properties of Waves
If you press down on a piano key,
let's say middle C, it generates a sound wave. Now, imagine that you press it down much harder
so that it still plays the same tone but more loudly. How would pressing the key down harder change the sound wave
produced?
a. | The sound wave's frequency would increase. | b. | The sound
wave's amplitude would be larger. | c. | The sound wave's wavelength would
increase. | d. | The sound wave's energy would decrease. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Stnd 06: Properties of Waves
SEP: Use mathematics and computational
thinking (compute wavelength) The speed of a wave is 33 m/s, and the frequency of this 17
Hz. What is the wavelength? (round to the nearest hundredth)
a. | wavelength is 1.94 Hz | c. | wavelength is .52 m. | b. | wavelength is 561 m. | d. | wavelength is 1.94
m. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Stnd 07: Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves
You are using a
telescope to look up into the night sky, and you observe a blinking light from a satellite in orbit
around the Earth. What logical
conclusion can you make about the properties of light from this observation?
a. | Light can travel through a vacuum. It can also travel through any
medium. | b. | Light cannot travel through vacuums, but it can travel through solids, liquids, and
gases | c. | Light can travel through a vacuum. It can also travel through a
gas. | d. | Light travels at 186, 000 miles per second. It can travel through some
mediums. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Stnd 07: Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves
A ray of light shines
through a transparent window. Next it shines through a transparent glass cup containing water and a
straw in it. You notice that the straw in the water appears to be misshaped. The light shining
through the glass next impacts a mirror on the far side of the room. Diagram 01 | Diagram 02 | Diagram 03 | Diagram 04 | | | | | | | | |
Two-Part Question
Part One: Place the diagrams
in the correct sequence to match the provided narrative above. Part Two: Identify the type
of wave: Mechanical or Electromagnetic?
a. | Part One: Diagram 01, Diagram 02, Diagram 03
Part Two: Visible light is an
electromagnetic wave | b. | Part One: Diagram 02, Diagram 04, Diagram
03
Part Two: Visible light is a mechanical wave | c. | Part One: Diagram 03, Diagram 04, Diagram
02
Part Two: Visible light is an electromagnetic wave | d. | Part One: Third
Diagram, 1st Diagram, Second Diagram
Part Two: Visible light is a form of solar
radiation |
|
|
|
16.
|
Stnd 08: Waves in Communication Systems
An air traffic controller
monitoring radar signals determines that an aircraft is flying at the wrong altitude. She
communicates with the airplane’s pilot via radio to alert them about this.
Which two
kinds of waves was the air traffic controller using, and what kind of waves are they?
a. | Microwaves and Gamma Rays. Microwaves and gamma waves are
mechanical. | b. | Radar waves and Radio. Radar is mechanical. Radio waves are
electromagnetic. | c. | Microwaves and Visible Light waves. Both of these are electromagnetic
waves. | d. | Microwaves and Radio waves. Both of these are electromagnetic
waves. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Stnd 08: Waves in Communication Systems
Fiber optic cables have
greatly improved communication systems by increasing the bandwidth for data/images to be
transmitted. Which kinds
of waves are used with fiber optic cables, and how fast can waves propagate through these
cables?
a. | Fiber optic cables use infrared waves at the speed of light. | b. | They use ultraviolet
waves that move at the speed of light. | c. | They use a combination of radio waves and sound
waves at the speed of sound. | d. | They use visible light waves that move at the
speed of light. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Stnd 02: Non-Contact Forces
Examine the
apparatus shown in the illustration containing two circular magnets. Notice that magnet A is
levitating above magnet B due to a non-contact force.
Illustration A |
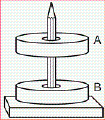
t | |
Which of the following statements
correctly describes what is happening in this diagram?
a. | The bottom of magnet A is a north pole, and the bottom
of magnet B is also a north pole. This is showing magnetic attraction (opposites
attract). | b. | The polarity of the top of magnet B is the opposite
polarity of the bottom of magnet A. This is showing wave refraction (waves
bending). | c. | The polarity at the top of magnet B is the same as the
polarity at the bottom of magnet A. This is showing magnetic repulsion (like
repels). | d. | The top of magnet B is positively charged, and the
bottom of magnet A is also positively charged. This is showing electrostatic repulsion (opposites
attract). |
|
|
|
19.
|
Stnd 02: Non-Contact Forces
Two students
decided to use their knowledge about non-contact forces to build a hoverboard park. They embedded
thousands of bar magnets into the surface of the floor with the north poles facing up.
Hoverboard Skatepark | t | |
What would the
polarity of the bottom of the hoverboard have to be in order to overcome the non-contact force of
gravity (to levitate the board), and what kind of non-contact force would this
demonstrate?
a. | ---Instead of magnets, they could simply mount wheels on
the board.
---This would demonstrate electrostatic
force. | b. | ---Hoverboards would not have any polarity since they
are made of aluminum.
---This would demonstrate nuclear
forces. | c. | ---The bottom of the hoverboard would have to be a south
pole.
---This would demonstrate
gravity. | d. | ---The bottom of the hoverboard would have to be a north
pole.
---This would demonstrate
magnetism. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Stnd 02: Non-Contact Forces
The
first satellite was launched into orbit in 1957. Today there are over 2000 satellites in orbit.
.
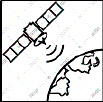 . . | |
Two-Part
Question
Part One: Which non-contact force
keeps these satellites from being flung out into space as they orbit planet Earth?
Part Two:
Is this non-contact force attractive of repulsive?
a. | Part One: Magnetism is the non-contact forces
that keeps satellites in orbit.
Part Two: Magnetism is a repulsive (pushing) force.
| b. | Part One: Gravity is the non-contact forces that
keeps satellites in orbit.
Part Two: Gravity is a repulsive (pushing) force.
| c. | Part One: Gravity is the non-contact forces that
keeps satellites in orbit.
Part Two: Gravity is an attractive (pulling) force.
| d. | Part One: Electrostatic forces keeps satellites
in orbit around our planet..
Part Two: These forces are always attractive (pulling force).
|
|
|
|
21.
|
Stnds 01/23:
Electromagnetism
Examine the two models of
electromagnets shown below.
A group of students constructed a model of an electromagnet which
was able to lift two paper clips (see Model W above).
1) Ask Questions:
How does electricity moving through the wire
convert the nail into a temporary magnet? | 2) Define Problems:
Model W can only lift two paper
clips. What change would enbable it to lift more paper clips? | |
a. | 1) Electrical current forms a magnetic field which
realigns the atoms in the nail.
2) One solution is to add more
coils to the iron core (see Model X above). | b. | 1) A non-contact
force (nuclear strong force) forms a magnetic field in the nail.
2) To solve this problem, they could use a plastic or glass core (see Model
X). | c. | 1) The electrostatic force is reflected through the wire
causing diffusion of energy.
2) One solution to this problem
is to move the batteries further away from the nail. | d. | 1) A non-contact force (gravitational attraction) realigns the atoms in the
nail.
2) One solution to this problem is to add more batteries
to the model. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Stnds 01/23: Electromagnetism
Design
Task-Using 50 centimeters of copper wire, a bar magnet, and an amperage gauge, construct a device
that will induce electrical current (build an electrical generator).
Which one of these models successfully
accomplished the design task, and what is wrong about the other three models?
a. | Model Beta is an electromagnet. All other models merely show magnetic
fields. | b. | Model Beta is an electrical generator. The other models merely show
magnets. | c. | Model Delta is inducing electricity. The other models merely show magnetic
fields. | d. | Model Alpha is demonstrating magnetic attraction. All other models display
repulsion. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Stnd 23: A team of four students were asked
to create a model of an electrical generator. Each team member created one model displaying
electromagnetic phenomenon (see pictures below).
Select the model shown below that is
demonstrating electricity being induced.
|
Multiple Response
Identify one
or more choices that best complete the statement or answer the question.
|
|
|
24.
|
Stnd 03: Kinematics Free-body diagrams show the magnitude and
direction of all forces acting on an object. Multi-Select QuestionSelect the answer choices below
that describe the motion of the object represented in the Free Body Diagram above (Select 2
choices).
|
|
|
25.
|
Stnd 06: Examine the sine pattern diagram shown below. (Multi-Select Question)
Select
three choices that correctly match the letters shown in the diagram above?
|
|
|
26.
|
Stnd 01: Magnetism and Electricity
MRI machines use magnetic fields from powerful electromagnets to create images
of the inside of a person’s body (see diagram below).
Magnetic
Resonance Imaging
(MRI) | | |
(Multi-Select Question)
How are the electromagnets in a MRI machine similar to all other
electromagnets, and how could a doctor increase a MRI machines’ magnetic field
(Select two
choices).
|
|
|
27.
|
Stnd 02: Non-Contact Forces
Non-contact forces can be either attractive or
repulsive.
Picture
01 | Picture 02 | Picture 03 | Picture 04 | | | | | | | | |
A student was asked to demonstrate that
fields exist between objects exerting forces on each other even though the objects are not in
contact. The results of this demonstration are shown above.
(Multi-Select Question) Select two pictures that show repulsion, and determine which kind of
non-contact force these pictures are displaying. (Select two choices).
|
|
|
28.
|
Stnd 04: 2nd Law of MotionOn Earth an astronaut weighs 980 Newtons
(about 220 pounds) and has a mass of 100 kilograms. On the Moon, the same astronaut weighs 162.2
Newtons (about 37 pounds). (Multi-Select Question) What is the mass of this astronaut on the
Moon, and what is the acceleration acting on the astronaut’s body when she is standing on the
Earth? (select 2 choices)
|