Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A combination of components that work together to form a unit is a(n)
____.
A. | system | B. | subsystem | C. | armature | D. | cycle |
|
|
|
2.
|
A(n) ____ system transfers power from one point to another through mechanical
motion that is used to do work.
A. | sensing | B. | optoelectronic | C. | timing | D. | electromechanical |
|
|
|
3.
|
When subsystems are combined, the result is referred to as a ____.
A. | cycle | B. | synthesized system | C. | transmission
path | D. | digital system |
|
|
|
4.
|
The process of converting alternating current power to direct current is called
____.
A. | work | B. | control | C. | rectification | D. | cycle timing |
|
|
|
5.
|
____ devices operate within the transmission path and alter the flow of
power.
A. | Control | B. | Load | C. | Cycle | D. | Commutator |
|
|
|
6.
|
The ____ is a subsystem that displays information about operating conditions at
points throughout the system.
A. | timing | B. | control | C. | channel | D. | indicator |
|
|
|
7.
|
Control in mechanical systems is accomplished by changing ____.
A. | pressure | B. | direction | C. | speed | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
8.
|
In electrical systems, a ____ system signals a response to a particular form of
energy.
A. | timing | B. | sensing | C. | control | D. | power |
|
|
|
9.
|
A(n) ____ system provides a lapse in time before the load device becomes
energized.
A. | cycle timing | B. | interval timing | C. | delay
timing | D. | All of the above. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The ____ unit of an industrial robot determines its flexibility and
efficiency.
A. | timing | B. | control | C. | sensing | D. | power |
|
|
|
11.
|
In a closed-loop system, the signal or data that provides information about
interaction between the control unit and the load is called ____.
A. | feedback | B. | cycle timing | C. | comparator | D. | slip |
|
|
|
12.
|
The ____ compares the feedback signal from the controlled element to a reference
signal or standard.
A. | end effector | B. | rotor | C. | controller | D. | comparator |
|
|
|
13.
|
The rotary motion, or turning force, of an electric motor is called ____.
A. | work | B. | friction | C. | torque | D. | feedback |
|
|
|
14.
|
The ____ is the rotating component of a motor and includes the armature, shaft,
and associated parts.
A. | stator | B. | rotor | C. | commutator | D. | detector |
|
|
|
15.
|
The coil wires wrapped around the electromagnets in the stator are called
____.
A. | field windings | B. | brushes | C. | flux | D. | mechanical
fuses |
|
|
|
16.
|
As the mechanical load on a dc motor increases, the motor speed ____.
A. | increases | B. | decreases | C. | stays the
same | D. | cannot be measured |
|
|
|
17.
|
A ____ dc motor has two sets of field windings.
A. | shunt-wound | B. | permanent-magnet | C. | series-wound | D. | compound-wound |
|
|
|
18.
|
A ____ motor has a solid rotor, called a squirrel cage rotor.
A. | universal | B. | three-phase synchronous | C. | single-phase
induction | D. | dc stepping |
|
|
|
19.
|
The difference between the synchronous speed and the rotor speed is called
____.
A. | torque | B. | slip | C. | cemf | D. | flux |
|
|
|
20.
|
____ systems are machines that change the position or speed of a mechanical
object in response to system feedback.
A. | Servo | B. | Synthesized | C. | Synchronous | D. | Timing |
|
|
|
21.
|
A(n) ____ motor is comprised of a rotor and a stator assembly, and contains no
brushes, commutators, or slip rings.
A. | universal | B. | dc stepping | C. | induction | D. | synchronous |
|
|
|
22.
|
DC stepping motors are primarily used to change electrical pulses into
____.
A. | dc power | B. | feedback signals | C. | rotary
motion | D. | input commands |
|
True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
23.
|
Work occurs when energy is transformed into mechanical motion, heat, light,
chemical action, or sound.
|
|
|
24.
|
The most common source of power for synthesized systems is alternating current
(ac).
|
|
|
25.
|
Single-phase ac power consists of three alternating currents that vary by
120°.
|
|
|
26.
|
Examples of loads include digital meters, pressure gauges, tachometers, and
thermometers.
|
|
|
27.
|
The transmission path provides a channel for the transfer of energy.
|
|
|
28.
|
In a mechanical system, control is accomplished by changing pressure, direction,
force, and speed.
|
|
|
29.
|
Timing systems convert electrical energy into mechanical motion.
|
|
|
30.
|
Open-loop control systems use sequencers and mechanical stops to control the end
point positions of the robot arm.
|
|
|
31.
|
A digital system is a set of components that work together to process numeric
information.
|
|
|
32.
|
In an electric motor, the armature is an electromagnet.
|
|
|
33.
|
The counter electromotive force flows against the voltage coming into a dc
motor.
|
|
|
34.
|
Horsepower is a measure of the amount of current produced over a specified
amount of time.
|
|
|
35.
|
In a series-wound dc motor, the armature and field circuits are connected in a
series arrangement.
|
|
|
36.
|
In bifilar construction, three separate wires are simultaneously wound into the
stator coil slots.
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
37.
|
In a mechanical system, ______________________________ measure physical
quantities, such as pressure, speed, and force.
|
|
|
38.
|
The ______________________________ of a sensing system outputs a signal that is
used to control the load device.
|
|
|
39.
|
The ______________________________ receives data from both the input source and
the output device, and determines if a correction signal should be sent to the actuator.
|
|
|
40.
|
A(n) ______________________________ motor is the only dc motor that can also be
operated using ac power.
|
|
|
41.
|
______________________________ occurs when energy is transformed into mechanical
motion, light, heat, chemical action, or sound.
|
|
|
42.
|
In an automated system, the part(s) designed to produce work is referred to as
the ______________________________.
|
|
|
43.
|
______________________________ timing systems may include both interval and
delay timing to provide energizing action in an operational sequence.
|
|
|
44.
|
Flexible, fiber-optic rods that transfer light energy from its source to distant
locations are called ______________________________.
|
|
|
45.
|
As the armature of a dc motor rotates, it generates its own voltage called
______________________________.
|
|
|
46.
|
The ______________________________ rating of a motor represents the power of the
motor.
|
|
|
47.
|
Examples of ______________________________ in automated systems include electric
motors, heating systems, lighting systems, alarms, and mechanical actuators.
|
|
|
48.
|
A ______________________________ open-loop system simply turns the system off or
on.
|
|
|
49.
|
The ______________________________ is the rotating part of a motor that creates
torque.
|
|
|
50.
|
Changes in the field current result in corresponding changes in the
______________________________ of the electromagnetic field.
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each system listed with its function or description. A. | Timing systems | B. | Digital systems | C. | Sensing
systems | D. | Synthesized systems | E. | Mechanical systems | F. | Control
systems | G. | Servo systems |
|
|
|
51.
|
Continually at work making adjustments that alter machine operation.
|
|
|
52.
|
Signal a response to a particular form of energy.
|
|
|
53.
|
Produce some form of mechanical motion.
|
|
|
54.
|
Ensure that all actions of an operation occur at a precisely defined
interval.
|
|
|
55.
|
Machines that change the position or speed of a mechanical object.
|
|
|
56.
|
Numeric instructions are changed into a series of on/off electrical
signals.
|
|
|
57.
|
The combination of multiple subsystems.
|
|
|
Identify the basic parts of a dc motor.
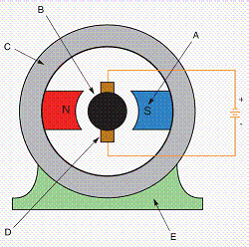
|
|
|
58.
|
Mounting
|
|
|
59.
|
Field pole
|
|
|
60.
|
Brush-commutator assembly
|
|
|
61.
|
Stator
|
|
|
62.
|
Rotor
|