Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The five main components of an industrial robot include which of the
following?
A. | Pneumatic drive | B. | Tachometer | C. | Work
envelope | D. | Means for programming |
|
|
|
2.
|
A controller has ____ levels of hierarchical control.
|
|
|
3.
|
The highest hierarchical control level is ____ control.
A. | actuator | B. | main | C. | path | D. | base |
|
|
|
4.
|
The ____ provides the energy to drive the robot’s controller and
actuators.
A. | program | B. | power supply | C. | servo
amplifier | D. | None of the above. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following is an example of a means for programming?
A. | Teach pendant | B. | Teach box | C. | Hand-held
programmer | D. | All of the above. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A robot’s ability to move up and down, forward and backward, and to the
left and right is described as the robot’s ____.
A. | trajectory | B. | work envelope | C. | degrees of
freedom | D. | manipulator segments |
|
|
|
7.
|
The vertical traverse provides ____ motion of a robot’s arm.
A. | up-and-down | B. | side-to-side swivel | C. | extending and
retracting | D. | point-to-point |
|
|
|
8.
|
In a(n) ____ system, no feedback mechanism is used to compare programmed
position to actual positions.
A. | servo | B. | open-loop | C. | closed-loop | D. | direct-drive |
|
|
|
9.
|
A servo robot is a(n) ____ system because it allows for feedback signals.
A. | servo | B. | open-loop | C. | closed-loop | D. | direct-drive |
|
|
|
10.
|
Three types of motors commonly used for ____ actuator drives include ac servo
motors, dc servo motors, and stepper motors.
A. | hydraulic | B. | pneumatic | C. | linear | D. | electric |
|
|
|
11.
|
A(n) ____ drive system uses fluid and consists of a pump connected to a
reservoir tank, control valves, and an actuator.
A. | hydraulic | B. | pneumatic | C. | direct | D. | electric |
|
|
|
12.
|
The shape of a robot’s work envelope is determined by the ____.
A. | type of coordinate system | B. | arrangement of joints | C. | length of the
manipulator’s segments | D. | All of the
above. |
|
|
|
13.
|
A robot arm using the ____ configuration can start and stop simultaneously along
the X, Y, and Z axes.
A. | cylindrical | B. | Cartesian | C. | revolute | D. | spherical |
|
|
|
14.
|
The ____ configuration consists of two orthogonal slides placed at a 90° angle and mounted on a rotary axis.
A. | cylindrical | B. | Cartesian | C. | revolute | D. | spherical |
|
True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
15.
|
The power supply of a robotic system may convert ac voltage to the dc voltage
required by a robot’s circuits.
|
|
|
16.
|
The five major components of industrial robots are the controller, manipulator,
end effector, base, and workpiece.
|
|
|
17.
|
Robot movement is initiated by a series of instructions stored in the end
effector.
|
|
|
18.
|
Hierarchical control organizes commands from the software to the parts of a
robot into layers.
|
|
|
19.
|
Linear actuators provide rotary motion to a robot’s arm.
|
|
|
20.
|
The end effector is attached to the end of the robot arm.
|
|
|
21.
|
Pitch is the side-to-side movement of a robot’s wrist.
|
|
|
22.
|
The operations of a robot with seven degrees of freedom are less complex than
the operations of a robot with three degrees of freedom.
|
|
|
23.
|
A non-servo robot is a closed-loop system.
|
|
|
24.
|
A servo amplifier translates signals from the controller into motor voltage and
current signals.
|
|
|
25.
|
Hydraulic actuator drives provide precise motion control and can handle heavy
loads.
|
|
|
26.
|
The four major work envelope configurations are revolute, Cartesian, spherical,
and open.
|
|
|
27.
|
The work envelope of a robot using a Cartesian configuration is rectangular in
shape.
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
28.
|
The ______________________________ is the part of a robot that coordinates all
movements of the mechanical system.
|
|
|
29.
|
The three basic levels of hierarchical control are actuator control, path
control, and ______________________________ control.
|
|
|
30.
|
The arm of a robot that moves materials, parts, or tools is the
______________________________.
|
|
|
31.
|
Rotary motion can be converted to ______________________________ using a lead
screw or other means of mechanical conversion.
|
|
|
32.
|
A(n) ______________________________ measures the acceleration and deceleration
of the manipulator.
|
|
|
33.
|
The ______________________________ is the robot’s hand.
|
|
|
34.
|
The extending and retracting movement of a robot arm is an example of
______________________________ traverse motion.
|
|
|
35.
|
The movements of ______________________________ configuration robots closely
resemble those of the human body.
|
|
|
36.
|
Three common characteristics used to classify robots are type of
______________________________, type of actuator drive, and shape of the work envelope.
|
|
|
37.
|
The simplest type of robot is a(n) ______________________________ robot, also
called a limited sequence robot.
|
|
|
38.
|
In a(n) ______________________________ system, a feedback signal affects the
output of the system.
|
|
|
39.
|
A(n) ______________________________ actuator drive system operates using
compressed air.
|
|
|
40.
|
The ______________________________ configuration is ideally suited for
pick-and-place operations, but has reduced repeatability and accuracy.
|
|
|
41.
|
The movement of a(n) ______________________________ configuration robot
resembles the action of the turret on a military tank.
|
|
|
42.
|
A(n) ______________________________ configuration is horizontally articulated
and generally has one vertical and revolute joints.
|
Matching
|
|
|
Identify the degree of freedom depicted in each illustration. Answers are
used only once.
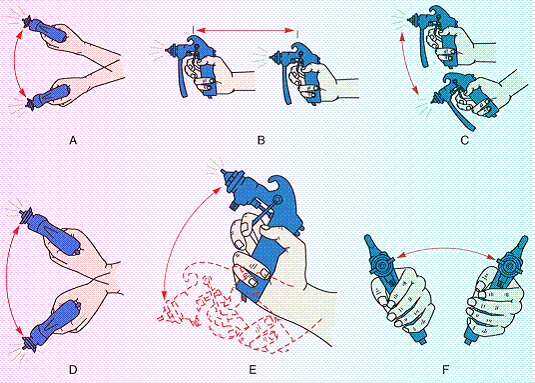
|
|
|
43.
|
Pitch
|
|
|
44.
|
Vertical traverse
|
|
|
45.
|
Rotational traverse
|
|
|
46.
|
Roll
|
|
|
47.
|
Yaw
|
|
|
48.
|
Radial traverse
|
|
|
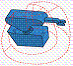
Identify the configuration of each work envelope illustration. Answers may be
used more than once. A. | Revolute | B. | Cartesian | C. | Spherical | D. | Cylindrical |
|
|
|
49.
|
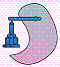
|
|
|
50.
|
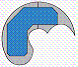
|
|
|
51.
|
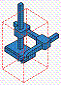
|
|
|
52.
|

|
|
|
53.
|
|