Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The net area over which the pressure acts when retracting a double-acting
cylinder can be found by subtracting the rod area from the _____________ area.
a. | piston | c. | cam | b. | surface area | d. | bushing |
|
|
|
2.
|
Pascal’s Law applies only to ___________.
a. | high octane fluids | c. | confined fluids | b. | gases | d. | fluids in
motion |
|
|
|
3.
|
Pneumatic leverage refers to the ability of a pneumatic system to develop a
large force output with ___________.
a. | a crowbar | c. | absolute force input | b. | a low force input | d. | hydraulic fluid |
|
|
|
4.
|
To convert gauge pressure to absolute, _______________.
a. | add atmospheric pressure to the gauge pressure | c. | add 101kPa to the kPa gauge
reading | b. | add 14.7 psi to the psig reading | d. | All of the
above |
|
|
|
5.
|
An air compressor creates ______________.
a. | flow | c. | pressure | b. | gas | d. | 14.7 psi |
|
|
|
6.
|
Boyle’s Law states that __________________.
a. | pressure in a confined volume is equal | c. | pressure is inversely proportional
to volume | b. | pressure is force intensity | d. | volume is directly proportional to pressure |
|
|
|
7.
|
Flow occurs between two connected points in a pneumatic system when
_____________.
a. | there is a vacuum | c. | there is a high pressure | b. | a pressure
differential exists | d. | pressure is the same at both points |
|
|
|
8.
|
The two types of resistance to air flow in a pneumatic system are
_______________.
a. | actuator load and atmospheric pressure | c. | weight and
torque | b. | pressure and area | d. | friction and actuator load |
|
|
|
9.
|
 P is the difference in pressure between
_______________. a. | absolute and gauge pressure | c. | two points in a pneumatic
system | b. | the cylinder and the rod | d. | four points in a pneumatic system |
|
|
|
10.
|
Pressure beyond that to overcome all resistive load determines
___________.
a. |  P P | c. | actuator speed | b. | Actuator
force | d. | back
pressure |
|
|
|
11.
|
The force output of a cylinder when extending can be calculated by multiplying
the pressure by the ____________ area.
a. | rod | c. | piston | b. | annular | d. | stroke |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Segment 1
a. | 14.8; 65.8 | e. | 1005;
4511 | b. | 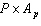 | f. | rod | c. | greater
retract | g. | spring | d. | 943; 4231 |
|
|
|
12.
|
The formula for force output of a cylinder during extension is
__________.
|
|
|
13.
|
The annular area of a cylinder is less than the cap-end (piston area) because
of the ____________.
|
|
|
14.
|
A(n) ___________ can be used to measure the actual force output of a
cylinder.
|
|
|
15.
|
To compress a spring with a K value of 45 lbs/in (7.9 N/mm), a total distance
of 21/64ths inches (8.33 mm) would take _______lbs/______ Newtons of force.
|
|
|
16.
|
A 4 in/10.2 cm diameter cylinder with a 1in/2.54 cm diameter rod will provide a
theoretical push force of ______lbs/ ______ N at 80 psi / 552 kPa.
|
|
|
17.
|
The theoretical pull (retraction) force that the cylinder in question 5 (in
matching) would provide is ________lbs _________N.
|
|
|
18.
|
A smaller cylinder rod in the example of question 5 (in matching) would provide
a(n) _________ force.
|
|
|
Segment 2
a. | 62.5 | e. | calibration | b. | 375 | f. | stalled | c. | force | g. | high | d. | confined |
|
|
|
19.
|
Pascal’s Law states that pressure on a(n) ________ fluid is transmitted
undiminished to every portion of a container.
|
|
|
20.
|
Pneumatic actuators may be __________ indefinitely without damage.
|
|
|
21.
|
Using pneumatic leverage, ______ is multiplied.
|
|
|
22.
|
One significance of Pascal’s Law is that it makes it possible for
pneumatic systems to generate a(n) _________ force with a(n) low input pressure to move a
load.
|
|
|
23.
|
75 psi acting across an area of five square inches produces _______ lbs of
force.
|
|
|
24.
|
The pressure needed to produce 500 lbs of force on an eqight square inch area
is ________ psi.
|
|
|
25.
|
A procedure called _________ is required in order to set gauges
accurately.
|
|
|
Segment 3
a. | atmospheric | e. | 101 | b. | inversely | f. | air compressor | c. | Gauge | g. | 44.1 | d. | Absolute |
|
|
|
26.
|
The absolute pressure at sea level is 14.7 psi / ________kPa.
|
|
|
27.
|
To convert gauge pressures to absolute, add _________ to the gauge
pressure.
|
|
|
28.
|
_____________ pressures are used in the formula defining Boyle’s
Law.
|
|
|
29.
|
_____________ pressure indicates the amount of pressure above atmospheric
pressure.
|
|
|
30.
|
Boyle’s Law states that pressure is ____________ proportional to
volume.
|
|
|
31.
|
4 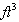 of atmospheric air compressed to 1 of atmospheric air compressed to 1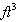 will be at _______ psig. will be at _______ psig.
|
|
|
32.
|
The machine used to compress air is called a(n) _______________.
|
|
|
Segment 4
a. | speed | d. | difference | b. | sound | e. | downstream | c. | pressure
difference |
|
|
|
33.
|
Air will flow when there is a(n) ______________.
|
|
|
34.
|
Delta P is the _________ in pressure between two points in a pneumatic
system.
|
|
|
35.
|
Increasing the air pressure to an actuator as it is moving a load will increase
the _______________.
|
|
|
36.
|
The maximum speed of air flow occurs at the speed of __________.
|
|
|
37.
|
DP allows you to describe the resistance of a component regardless of the
___________ pressure.
|