True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
|
|
|
2.
|
Electric Generators convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
|
|
|
3.
|
In a Brushless DC Motor, the rotor is a permanent magnet.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
4.
|
This is a _________. 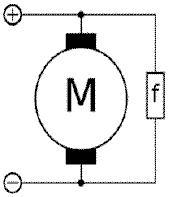 a. | DC Series Motor | c. | DC Compound Motor | b. | DC Shunt Motor | d. | Induction Motor |
|
|
|
5.
|
This is a _________. 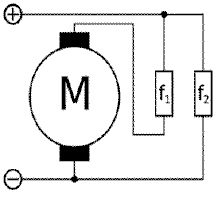 a. | DC Series Motor | c. | DC Compound Motor | b. | DC Shunt Motor | d. | Induction Motor |
|
|
|
6.
|
This is a _________. 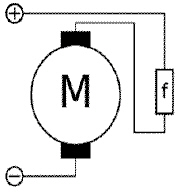 a. | DC Series Motor | c. | DC Compound Motor | b. | DC Shunt Motor | d. | Induction Motor |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which motor can set the number of degrees the shaft will rotate for each full
step?
a. | DC Series Wound Motor | c. | DC Permanent Magnet Motor | b. | DC Shunt Wound
Motor | d. | Stepper
Motor |
|
|
|
8.
|
This is a ____________.  a. | Brushless DC Motor Stator | c. | Induction Motor
Stator | b. | Permanent Magnet DC Motor Stator | d. | Compound Motor
Stator |
|
|
|
9.
|
This is a ____________.  a. | Brushless DC Motor rotor | c. | Induction Motor
rotor | b. | Permanent Magnet DC Motor rotor | d. | Compound Motor
rotor |
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | Constant Torque Loads | c. | Constant Power Loads | b. | Variable Torque
Loads |
|
|
|
10.
|
Torque varies inversely with speed.
|
|
|
11.
|
Torque varies with square operation of speed.
|
|
|
12.
|
Output power varies but torque is constant.
|
|
|
a. | Field Windings | d. | Brushes | b. | Commutator Segments | e. | Armature Windings | c. | Interpole
Windings |
|
|
|
13.
|
Pieces of carbon or graphite pushed against a spring to maintain electrical
contact with the commutator segments.
|
|
|
14.
|
The windings in the rotor.
|
|
|
15.
|
The winding that is on the stator, unless it is a permenant magnet
motor.
|
|
|
16.
|
A third set of windings are mounted on the stator in series with the rotor to
reduce the sparking between brushes and the commutator.
|
|
|
17.
|
The method to convert the DC current to an alternating current in the rotor of
a DC motor.
|
|
|
a. | DC Series Wound | c. | DC Shunt Wound | b. | DC Compound
Wound |
|
|
|
18.
|
Good Torque and stable speed
|
|
|
19.
|
Highest Starting Torque
|
|
|
20.
|
Motor Speed Control
|