True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Capacitance is the ability to store voltage.
|
|
|
2.
|
A capacitor blocks dc and
passes ac.
|
|
|
3.
|
When two capacitors are
connected in parallel across a dc source, the smaller capacitor drops the larger
voltage.
|
|
|
4.
|
If the distance between the
plates of a capacitor increases, the capacitance decreases.
|
|
|
5.
|
A capacitor can fully charge in
one time
constant.
|
|
|
6.
|
A capacitor will fully charge
in about five time constants.
|
|
|
7.
|
To find the total capacitance
of two capacitors in parallel, you must combine them using a similar procedure as resistors in
parallel.
|
|
|
8.
|
If the plate area of a
capacitor decreases, the capacitance decreases.
|
|
|
9.
|
The voltage rating of a
capacitor indicates the voltage it will charge up to.
|
|
|
10.
|
Leakage through a capacitor is
undesirable.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the capacitance of a capacitor that drops
50 V and stores 0.500 ìC of charge?
a. | 0.001 ìF | c. | 0.1
ìF | b. | 0.01 ìF | d. | 1
ìF |
|
|
|
12.
|
How much charge is stored in a 0.022 ìF
capacitor that drops 22 V?
a. | 0.0484 ìC | c. | 4.84
ìC | b. | 0.484 ìC | d. | 48.4
ìC |
|
|
|
13.
|
If a 0.05 ìF and 0.1 ìF capacitor are connected in parallel across a 20 V source, the total capacitance
equals ________ and each capacitor drops ________.
a. | 0.15 ìF, 10 V | c. | 0.05
ìF, 15 V | b. | 0.15 ìF, 20
V | d. | 0.10 ìF, 20 V |
|
|
|
14.
|
If a 0.022 ìF, 0.022 ìF and 0.05
ìF capacitor are connected in series across a 25 V source, the voltage drop
across the largest capacitor equals ________.
a. | 4.51 V | c. | 10.2 V | b. | 17.5 V | d. | 11.8 V |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is one time constant of a 4.7 ìF
capacitor in series with a 22 kÙ resistor?
a. | 1.03 ms | c. | 103 ms | b. | 0.103 ms | d. | 10.3 ms |
|
|
|
16.
|
How long will it take a 0.047 ìF capacitor to
fully charge through a 100 kÙ resistor?
a. | 2.35 s | c. | 0.235 ms | b. | 235 ms | d. | 23.5 ms |
|
|
|
17.
|
How long will it take a 1 ìF capacitor to
completely discharge through a 47 kÙ resistor?
a. | 235 ms | c. | 47 s | b. | 47 ms | d. | 235 s |
|
|
|
18.
|
If a 1 ìF capacitor and a 10 kÙ resistor
are connected in series across 20 VDC, approximately how much voltage will the
capacitor drop after charging for just one time constant?
a. | 17 V | c. | 11.0 V | b. | 12.6 V | d. | 12.1 V |
|
|
|
19.
|
If a 4.7 ìF capacitor and a 10 kÙ
resistor are connected in series across 25 VDC, approximately how much voltage
will the resistor drop after charging for just one time constant?
a. | 21.6 V | c. | 15.8 V | b. | 9.20 V | d. | 23.8 V |
|
|
|
20.
|
If a 4.7 ìF capacitor operates at 10 kHz,
XC equals ________.
a. | 3.39 Ù | c. | 294
ìÙ | b. | 339
Ù | d. | infinite Ù |
|
|
|
21.
|
At what frequency is a 2000
pF capacitor operating if its reactance is 745 Ù?
a. | 1.01
kHz | c. | 107
kHz | b. | 1010 Hz | d. | 10.1 kHz |
|
|
|
22.
|
If a 22 ìF capacitor is connected to a 15 V
400 Hz source, its current equals ________.
a. | 18.1 mA | c. | 1.81 A | b. | 55 mA | d. | 829 mA |
|
|
|
23.
|
If a 0.1 ìF, 0.1 ìF and 0.05 ìF capacitor are connected in series across a 75 V source, the voltage drop across the
smallest capacitor equals ________.
a. | 37.5 V | c. | 50 V | b. | 100 V | d. | 18.8 V |
|
|
|
24.
|
How long will it take to completely charge a 0.047
ìF capacitor through a 1 MÙ resistor?
a. | 0.47 s | c. | 0.235 s | b. | 0.029 s | d. | 0.047 s |
|
|
|
25.
|
If a 0.1 ìF capacitor and a 2.2 kÙ
resistor are connected in series across 30 VDC, how much voltage will the
capacitor drop after charging for just one time constant?
a. | 19.0 V | c. | 28.5 V | b. | 25.9 V | d. | 29.4 V |
|
|
|
26.
|
If the frequency applied to a
capacitor increases, the capacitive reactance ________.
a. | increases | c. | decreases | b. | remains the same | d. | varies up and down |
|
|
|
27.
|
A capacitor that transfers an
ac signal from one stage to another is called a ________ capacitor.
a. | bypass | c. | filter | b. | transfer | d. | coupling |
|
|
|
28.
|
If a 1 ìF, 2.2 ìF and 0.05 ìF
capacitor are connected in series, CT is less than ________.
a. | 0.05 ìF | c. | 2.2
ìF | b. | 1 ìF | d. | 0.001
ìF |
|
|
|
29.
|
If four 0.022 ìF
capacitors are connected in parallel, CT equals ________.
a. | 0.022 ìF | c. | 0.088
ìF | b. | 0.049 ìF | d. | 0.044
ìF |
|
|
|
30.
|
If an uncharged capacitor, a
resistor, a switch and a 12 V battery are connected in series, what is the voltage across the
capacitor at the instant the switch is closed?
|
|
|
31.
|
If an uncharged capacitor, a
resistor, a switch and a 12 V battery are connected in series, what is the voltage across the
capacitor after it is fully charged?
|
|
|
32.
|
If an uncharged capacitor, a
resistor, a switch and a 12 V battery are connected in series, at approximately what time will the
capacitor reach full charge?
a. | 5 × R ×
C | c. | 12 × R ×
C | b. | R ×
C | d. | The time cannot be
predicted. |
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the capacitance that stores 1.175 ìC
of charge and drops 25 V?
a. | 47 ìF | c. | 4.7
ìF | b. | 0.47 ìF | d. | 0.047
ìF |
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the minimum dc working
voltage rating for a capacitor that must drop 120 VRMS?
a. | 120 V | c. | 170 V | b. | 84.8 V | d. | 339 V |
|
|
|
35.
|
If a 0.047 ìF, 0.047 ìF and 0.47 ìF
capacitor are connected in series across a 25 V source, the total capacitance equals ________ and
each 0.047 ìF capacitor drops ________.
a. | 0.564 ìF, 1.2 V | c. | 0.564 ìF, 11.9 V | b. | 0.022 ìF, 25
V | d. | 0.022 ìF, 11.9 V |
|
|
|
36.
|
If a 22 ìF and 100 ìF capacitor are
connected in parallel across a 15 V source, the total capacitance equals ________ and the 22 ìF
capacitor drops ________.
a. | 1220 ìF, 30 V | c. | 18
ìF, 15 V | b. | 18 ìF, 5.2
V | d. | 122 ìF, 15 V |
|
|
|
37.
|
What is one time constant of a 47 ìF capacitor
in series with a 120 kÙ resistor?
a. | 0.564
ms | c. | 564
ms | b. | 5.64
s | d. | 54.6 s |
|
|
|
38.
|
How long will it take for a 22 ìF capacitor to
completely charge through a 47 kÙ resistor?
a. | 5.17 s | c. | 2.068 s | b. | 1.034 s | d. | 8.272 s |
|
|
|
39.
|
How long will it take for a 22 ìF capacitor to
completely discharge through a 4.7 kÙ resistor?
a. | 0.827 s | c. | 0.517 s | b. | 0.207 s | d. | 0.103 s |
|
|
|
40.
|
How much voltage is dropped across a 150 ìF
capacitor after 3.33 seconds if it is charged by a 50 V source through a 22 KÙ
resistor?
a. | 43.3 V | c. | 49 V | b. | 31.8 V | d. | 47.5 V |
|
|
|
41.
|
If a 0.047 ìF capacitor operates at 220 kHz,
XC equals ________.
a. | 1.54 kÙ | c. | 15.4
kÙ | b. | 154 Ù | d. | 15.4
Ù |
|
|
|
42.
|
At what frequency is a 0.001 ìF capacitor
operating if its reactance is 45 kÙ?
a. | 3.54
MHz | c. | 3.54
kHz | b. | 354 kHz | d. | 35.4 kHz |
|
|
|
43.
|
If a 47 ìF capacitor is connected to a 20 V,
400 Hz source, the current is ________.
a. | 0.851 A | c. | 2.36 A | b. | 8.51 A | d. | 425 A |
|
|
|
44.
|
When connecting a large
electrolytic capacitor to a circuit with a 100 VDC source, place the negative end of the capacitor
________.
a. | in either position; the polarity is
not important | b. | towards the positive side of the source | c. | towards the negative side of the
source |
|
|
|
45.
|
What is CT in Figure
9-1?
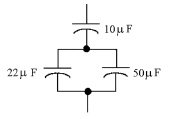
Figure 9-1
a. | 25.2 ìF | c. | 8.78
ìF | b. | 70.1 ìF | d. | 82
ìF |
|
|
|
46.
|
Electrolytic capacitors differ
from many other capacitors in construction in that they are:
a. | polarized. | c. | larger. | b. | sensitized. | d. | smaller. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Electrolytic capacitors must be
connected into a circuit such that:
a. | reversal of polarity does not
happen. | b. | positive lead to positive voltage; negative lead to negative
voltage. | c. | voltage rating marked is not exceeded. | d. | all of
these. |
|
|
|
48.
|
When capacitors are connected
in series, their total capacitance act like:
a. | resistance connected in
series-parallel. | c. | resistance
connected in series. | b. | resistance connected in parallel. | d. | all of these. |
|
|
|
49.
|
When capacitors are connected
in parallel, their total capacitance act like:
a. | resistance connected in
series-parallel. | c. | resistance
connected in series. | b. | resistance connected in parallel. | d. | all of these. |
|
|
|
50.
|
The time constant of a
capacitor is:
a. | directly proportional to the
resistance in the circuit. | b. | the time required to charge to 63% or discharge to
37%. | c. | directly proportional to the capacitance in the
circuit. | d. | all of these. |
|
|
|
51.
|
The time constant for a
capacitor for each time period is:
a. | 63% of the increase in
value. | c. | 37% of the decrease in
value. | b. | a constant factor. | d. | all of these. |
|
|
|
52.
|
In a capacitive AC circuit, the
phase relationship between the voltage and the current is such that the:
a. | voltage is leading the
current. | b. | current is 180 degrees out of phase with
voltage. | c. | voltage is 360 degrees out of phase with
current. | d. | current is leading the voltage. |
|
|
|
53.
|
A common use for electrolytic
capacitors found in power supplies is ________.
a. | blocking
DC | c. | decoupling | b. | passing AC | d. | filtering |
|
|
|
54.
|
A commonplace use for
capacitors in electronics is to:
a. | pass DC voltages
only. | c. | pass both AC and DC
voltages. | b. | block AC voltages. | d. | block DC voltages. |
|
|
|
55.
|
The removal of high frequency
transient voltages with a capacitor is called:
a. | coupling. | c. | ac blocking. | b. | decoupling. | d. | bypassing. |
|