True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
A sine wave's frequency
equals the reciprocal of its period.
|
|
|
2.
|
The higher a sine wave's
frequency, the shorter its period.
|
|
|
3.
|
A sine wave's peak value
is smaller than its RMS value.
|
|
|
4.
|
An ac current is inversely
proportional to an ac voltage.
|
|
|
5.
|
One complete sine wave contains
360°.
|
|
|
6.
|
RMS is another name for peak.
|
|
|
7.
|
7.07 VPP is approximately equal
to 2.5 VRMS.
|
|
|
8.
|
The term RMS stands for
"root-mean-square."
|
|
|
9.
|
The period of a 5 Hz wave form
is 200 ms.
|
|
|
10.
|
Commercial line voltages are
usually square waves at a frequency of 60 Hz.
|
|
|
11.
|
Current flows both ways
simultaneously in an AC circuit.
|
|
|
12.
|
Only frequency increases with
the speed of an AC generator.
|
|
|
13.
|
20 Vrms of alternating current
will illuminate a given lamp at the same intensity as 20 V of direct current.
|
|
|
14.
|
Rise time, fall time, and duty
cycle are all terms associated with sine wave measurement.
|
|
|
15.
|
Kirchhoff's voltage law
can be used with resistive ac circuits.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
16.
|
The RMS value of a sine wave means
________.
a. | the same as IP ×
R | b. | the same as IPP ×
R | c. | the root mean square
value | d. | the heating effect of an ac generator of the same
voltage |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the instantaneous
voltage at 42° on a 230 VP sine wave?
a. | 154 V | c. | 149 V | b. | 115 V | d. | 76.1 V |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which one of the following
represents the value at point G in Figure 8-1?
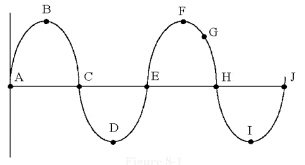
Figure 8-1
a. | the
frequency | c. | the
period | b. | the peak voltage | d. | the RMS voltage |
|
|
|
19.
|
which of the following can be
measured from points B to F in Figure 8-1?
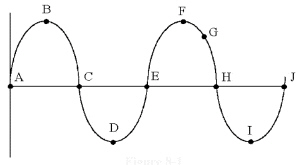
Figure
8-1
a. | the
angle | c. | the
frequency | b. | the peak-to-peak voltage | d. | the period |
|
|
|
20.
|
VPP is measured between points
________ in Figure 8-1.
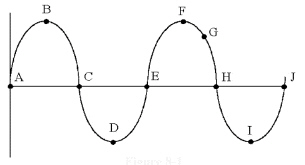
Figure
8-1
a. | C and H | c. | G and I | b. | D and F | d. | A and B |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which point in Figure 8-1 is
180° away from point E?
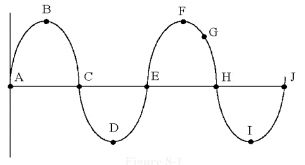
Figure
8-1
|
|
|
22.
|
In Figure 8-1, the time from
point C to E is called ________.
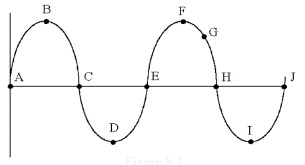
Figure
8-1
a. | a cycle | c. | peak voltage | b. | a half-cycle | d. | the period |
|
|
|
23.
|
In Figure 8-1, which of the
following can be measured from point E to point F?
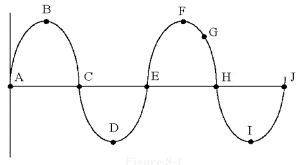
Figure 8-1
a. | the RMS
voltage | c. | the peak to peak
voltage | b. | one cycle of voltage | d. | the peak voltage |
|
|
|
24.
|
In Figure 8-1, if the time from
point A to H is 60 ìs the frequency is
________.
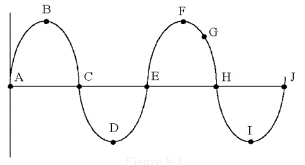
Figure 8-1
a. | 16.7
kHz | b. | 25 kHz | c. | 50 kHz | d. | More information is required to calculate the
frequency. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Calculate VR2 in Figure
8-2.
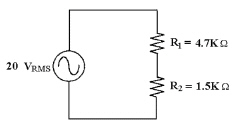
Figure 8-2
a. | 4.84 VP | c. | 13.15 VP | b. | 6.84 VP | d. | 6.84 VPP |
|
|
|
26.
|
What is the approximate peak
input voltage to the circuit in Figure 8-2?
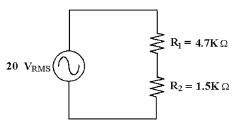
Figure
8-2
a. | 10 VP | c. | 28.3 VP | b. | 14.1 VP | d. | 20 VP |
|
|
|
27.
|
Calculate VR1 in Figure
8-2.
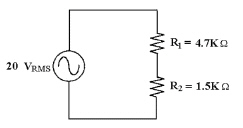
Figure 8-2
a. | 13.2 VP | c. | 6.84 VP | b. | 13.7 VP | d. | 21.4 VP |
|
|
|
28.
|
In Figure 8-2, what is the
instantaneous voltage across R1 at an angle of 22°?
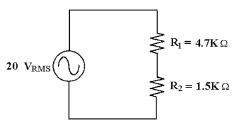
Figure 8-2
a. | 12.0 V | c. | 2.56 V | b. | 20.3 V | d. | 8.03 V |
|
|
|
29.
|
VR2 ________ if R1 opens in
Figure 8-2.
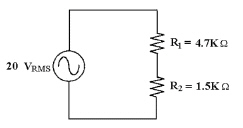
Figure 8-2
a. | remains the
same | c. | decreases | b. | increases |
|
|
|
30.
|
Find RT in Figure
8-2.
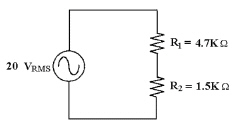
Figure 8-2
a. | 6.2
kÙ | c. | 4.7
kÙ | b. | 4.77 kÙ | d. | 1.13
kÙ |
|
|
|
31.
|
Find PR1 in Figure
8-2.
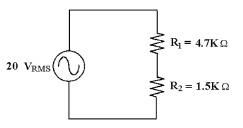
Figure 8-2
a. | 97.8 mW | c. | 0 W | b. | 196 mW | d. | 48.9 mW |
|
|
|
32.
|
If R1 shorts in Figure 8-2, VR2 ________.
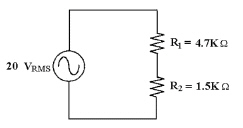
Figure 8-2
a. | increases | c. | decreases | b. | remains the same |
|
|
|
33.
|
In Figure 8-2, what is the
instantaneous voltage across R1 at 122°?
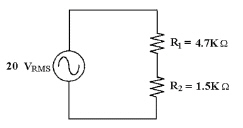
Figure 8-2
a. | 11.2 V | c. | 18.2 V | b. | 5.8 V | d. | 11.6 V |
|
|
|
34.
|
Calculate IT in Figure
8-2.
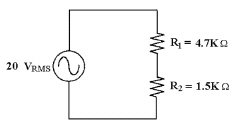
Figure 8-2
a. | 4.55
mAPP | c. | 3.22
mAPP | b. | 9.12 mAPP | d. | 6.44 mAPP |
|
|
|
35.
|
If you measure about 56 VPP
across the source in Figure 8-2, what is the trouble?
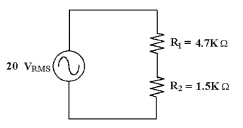
Figure 8-2
a. | R2 is
open. | b. | Both R1 and R2 are open. | c. | R1 is open. | d. | There is no trouble. 56 VPP is a normal measurement for
the source voltage. | e. | any of these |
|
|
|
36.
|
Calculate the total power
dissipation in the circuit in Figure 8-2.
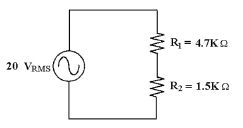
Figure
8-2
a. | 9.12 mW | c. | 182 mW | b. | 64.5 mW | d. | 45.6 mW |
|
|
|
37.
|
In Figure 8-2, if you look at
VR1 with an oscilloscope and you find no trace, a possible trouble might be that
________.
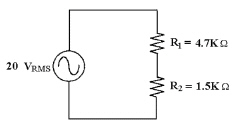
Figure 8-2
a. | R2 is
shorted | c. | R1 is
open | b. | R2 is open | d. | the resistance of R2 has changed |
|
|
|
38.
|
What is the instantaneous
voltage at 284° on a 22 VPP sine wave?
a. | -2.66 V | c. | 0.33 V | b. | 10.7 V | d. | -10.7 V |
|
|
|
39.
|
If a rectangular wave's
pulse width is 50 ìS and its frequency is 4 kHz, its duty cycle is
________.
a. | 98.75% | c. | 80% | b. | 20% | d. | 1.25% |
|
|
|
40.
|
The time required by a 10 V
square wave to change from 1 V to 9 V is known as the ________.
a. | rise
time | c. | fall
time | b. | pulse width | d. | period |
|
|
|
41.
|
What is the approximate
instantaneous voltage at 37° on a 169 VP sine wave?
a. | 239 V | c. | 102 V | b. | 135 V | d. | 119 V |
|
|
|
42.
|
A 60 Hz sine wave completes
________ cycles every 10 seconds.
|
|
|
43.
|
A 10 VP sine wave is equal to
________.
a. | 100 VPP | c. | 20 VPP | b. | 5 VPP | d. | none of the above |
|
|
|
44.
|
A sine wave's
instantaneous voltage is 0 V at ________ degrees.
a. | 360 | c. | 180 | b. | 0 | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
45.
|
If a 10 kÙ resistor carries 5 mARMS of current, its voltage drop equals
________.
a. | 70.7
VRMS | c. | 50
VRMS | b. | 5 VRMS | d. | 7.07
VRMS |
|
|
|
46.
|
In a two-resistor series
circuit VR1 = 6.5 VRMS and VR2 = 3.2 VRMS. The source voltage is ________.
a. | 4.53 VP | c. | 13.7 VP | b. | 9.19 VP | d. | 9.7 VP |
|
|
|
47.
|
A formula for VRMS is
________.
a. | 0.707 ×
VP | c. | 2.8 ×
VP | b. | 2 ×
VP | d. | 0.707 ×
VPP |
|
|
|
48.
|
What is the instantaneous
voltage at 17° on a 169 VP sine wave?
a. | 98.8 V | c. | 80.5 V | b. | 161 V | d. | 49.4 V |
|
|
|
49.
|
A 12 VP sine wave equals
________.
a. | 7.64
VAVG | c. | 24
VPP | b. | 8.48 VRMS | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
50.
|
An oscilloscope's
volts/division switch is set on 50 mV/div. If the vertical deflection of the oscilloscope's
trace is 1.6 division, what voltage is being measured?
a. | 80 mV | c. | 0.008 V | b. | 1.6 mV | d. | 50 mV |
|
|
|
51.
|
An oscilloscope's
seconds/division switch is set on 20 ms/div. If a sine wave measures 4 divisions horizontally, what
frequency is being measured?
a. | 25 Hz | c. | 50 Hz | b. | 12.5 Hz | d. | More information is needed. |
|
|
|
52.
|
An oscilloscope's
seconds/division switch is set on 20 ìs/cm. If the trace is 7.5 cm
long, what is the period?
a. | 0.0015
s | c. | 1.5 ìs | b. | 150 ìs | d. | 5 ìs |
|
|
|
53.
|
If the period of a square wave
is 22 ms, what is its frequency?
a. | 45.5
kHz | c. | 45.5
Hz | b. | 22
kHz | d. | 22 Hz |
|
|
|
54.
|
The symbol for the period of a
wave form is:
|
|
|
55.
|
The period of most AC waveforms
is measured in units of:
a. | cycles. | c. | alternations. | b. | revolutions. | d. | seconds. |
|
|
|
56.
|
The time (T) and the frequency
(f) of an AC waveform are related as:
a. | inversely
proportional. | c. | complimentary
proportional. | b. | directly proportional. | d. | universally proportional. |
|
|
|
57.
|
A square wave is a unique form
of the rectangular pulse wave in that:
a. | the positive and negative halves are
equal. | b. | the duty cycle is 50%. | c. | the wave is symmetrical. | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
58.
|
The formula to convert degrees
to radians is:
a. | degrees = 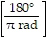 × radians.
× radians. | c. | radians =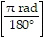 × degrees. × degrees. | b. | 180° = ð
radians. | d. | all of
these. |
|
|
|
59.
|
The largest numerical value in
the measurement of alternating current is:
a. | peak to
peak. | c. | rms. | b. | average. | d. | peak. |
|
|
|
60.
|
Troubleshooting an AC circuit
can be performed with which of the following tools?
a. | analog
voltmeter | c. | oscilloscope | b. | digital multimeter | d. | any of the above |
|
|
|
61.
|
Superimposing an AC voltage of
3.54 Vrms with a DC source of 10 V results in a waveform that:
a. | peaks at 15
V. | c. | peaks at 20
V. | b. | peaks at 13.54
V. | d. | both B and C |
|