True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
In a series circuit, the
current is the same at every point in the circuit.
|
|
|
2.
|
Kirchhoff's Voltage
Law states that the algebraic sum
of all the voltages around a closed path is zero.
|
|
|
3.
|
The total power dissipated in a
series circuit equals the sum of the individual powers.
|
|
|
4.
|
If 6.8 kÙ, 1.2 kÙ and 5.6 kÙ
resistors are wired in series, the total resistance is 13.6 kÙ.
|
|
|
5.
|
If 4.7 kÙ, 2.2 kÙ and 1.2 kÙ
resistors are wired in series, the total resistance is 8.7 kÙ.
|
|
|
6.
|
Total power dissipated in a
series circuit equals source voltage multiplied by current.
|
|
|
7.
|
If a resistor is rated at 1/2
W, it can safely dissipate 0.325 W.
|
|
|
8.
|
According to
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law,
the sum of the individual voltage drops in a series circuit equals the source
voltage.
|
|
|
9.
|
A series circuit has multiple
current paths.
|
|
|
10.
|
Three 2 V cells in series with
one in series-opposing would yield 2 V.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the total resistance in
Figure 4-1 if R1 = 10 kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ
and R3 = 15 kÙ?
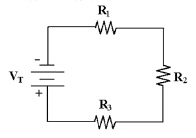
Figure 4-1
a. | 0
kÙ | c. | 35
kÙ | b. | 25 kÙ | d. | infinite
Ù |
|
|
|
12.
|
Calculate the current in Figure
4-1 if VR1 = 16 V, R1 = 10 kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ and R3 = 15 kÙ.
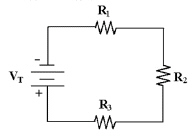
Figure 4-1
a. | 3.2 mA | c. | 12 mA | b. | 0 A | d. | 1.6 mA |
|
|
|
13.
|
Calculate VR2 and VR3 in Figure
4-1 if VR1 = 16 V, R1 = 10 kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ and R3 = 15 kÙ.
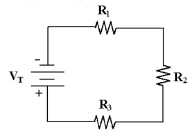
Figure 4-1
a. | VR2 = 16 V, VR3 = 16
V | c. | VR2 = 16 V, VR3 = 12
V | b. | VR2 = 24 V, VR3 = 12
V | d. | VR2 = 16 V, VR3 = 24
V |
|
|
|
14.
|
Calculate PR2 in Figure 4-1 if
VR1 =16 V, R1 = 10 kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ and
R3 = 15 kÙ.
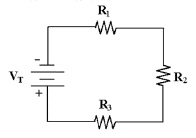
Figure
4-1
a. | 0.0256
mW | c. | 25.6
mW | b. | 2.56
mW | d. | 0.256 mW |
|
|
|
15.
|
Calculate VT in Figure 4-1 if
VR1 = 16 V, R1 = 10 kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ
and R3 = 15 kÙ.
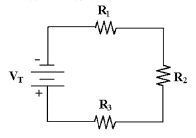
Figure 4-1
a. | 112 V | c. | 24 V | b. | 56 V | d. | 16 V |
|
|
|
16.
|
VR1 = 16 V, R5 = 10
kÙ, R2 = 10 kÙ and R3 = 15
kÙ in Figure 4-1. If R2 opens, then RT is
________.
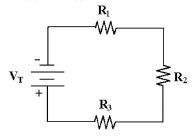
Figure 4-1
a. | 0
Ù | c. | 25
kÙ | b. | 10 kÙ | d. | infinite
Ù |
|
|
|
17.
|
If R2 opens in Figure 4-1, the
total power dissipated ________.
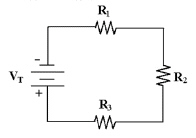
Figure
4-1
a. | remains the
same | c. | decreases to
zero | b. | increases to maximum | d. | will depend upon the source
voltage |
|
|
|
18.
|
Calculate PT in Figure 4-1 if
VT = 100 V and all three resistors are each 47 kÙ.
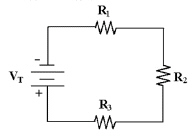
Figure 4-1
a. | 22 W | c. | 23.6 mW | b. | 70.9 mW | d. | 709 mW |
|
|
|
19.
|
Calculate VR3 in Figure 4-1 if
VT = 50 V, VR1 = 19.7 V and VR2 = 2.7 V.
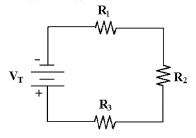
Figure
4-1
a. | 30.3 V | c. | 27.6 V | b. | 47.3 V | d. | 22.4 V |
|
|
|
20.
|
How much voltage is dropped
across R2 and R3 in Figure 4-1 if R1 = 4.7 kÙ, VR1 = 10 V, R2 = 4.7
kÙ and R3 = 4.7 kÙ?
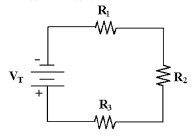
Figure 4-1
a. | VR2 = 4.7 V, VR3 = 10
V | c. | VR2 = 10 V, VR3 = 4.7
V | b. | VR2 = 10 V, VR3 = 10
V | d. | VR2 = 14.7 V, VR3 = 14.7
V |
|
|
|
21.
|
Calculate IT in Figure 4-1 if
R1 = 4.7 kÙ, VR1 = 10 V, R2 = 4.7 kÙ
and R3 = 4.7 kÙ.
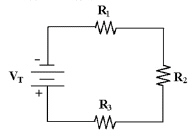
Figure 4-1
a. | 2.13 mA | c. | 1 mA | b. | 6 mA | d. | 4.26 mA |
|
|
|
22.
|
Calculate VT in Figure 4-1 if
R1 = 4.7 kÙ, VR1 = 10 V, R2 = 4.7 kÙ
and R3 = 4.7 kÙ.
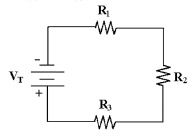
Figure 4-1
a. | 30 V | c. | 14.7 V | b. | 4.7 V | d. | 10 V |
|
|
|
23.
|
If R2 shorts in Figure 4-1, the
total circuit power ________.
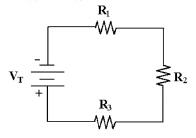
Figure
4-1
a. | remains the
same | c. | depends upon the source
voltage | b. | decreases | d. | increases |
|
|
|
24.
|
R1 = 4.7 kÙ, R2 = 4.7 kÙ and R3 = 4.7 kÙ in Figure 4-1. What is RT if R2 shorts?
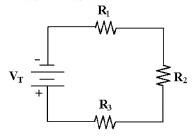
Figure 4-1
a. | 0
Ù | c. | 4.7
kÙ | b. | 9.4 kÙ | d. | infinite
Ù |
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the total supply
voltage if 16 V and 12 V sources are wired in series opposing?
|
|
|
26.
|
If 12 V and -19 V sources are
connected so their total voltage is -7 V, they are ________.
a. | in
parallel | c. | series
aiding | b. | series opposing | d. | connected dangerously |
|
|
|
27.
|
Based upon electron current
flow, the polarity on the side of the resistor where current enters is ________. The polarity on the
side of the resistor where current exits is ________.
a. | positive,
negative | c. | negative,
positive | b. | negative, negative | d. | positive, positive |
|
|
|
28.
|
When 50 V is applied to four
series resistors, 100 ìA flows. If R1 = 12 kÙ, R2 = 47 kÙ and R3 = 56 kÙ, what is the value of R4?
a. | 3.85
MÙ | c. | 38.5
kÙ | b. | 3.85 kÙ | d. | 385
kÙ |
|
|
|
29.
|
If R1 = 12 kÙ and R2 = 5 kÙ and they are wired in series across a 20
V source, what is VR1 and VR2?
a. | VR1 = 0 V, VR2 = 20
V | c. | VR1 = 14.12 V, VR2 = 5.88
V | b. | VR1 = 5.88 V, VR2 = 14.12
V | d. | VR1 = 10 V, VR2 = 10
V |
|
|
|
30.
|
Four resistors are connected in
series across an 18 V source. Three resistors drop 0 V and one resistor drops 18 V. What's the
trouble?
a. | The three resistors are
open. | b. | One resistor is open. | c. | Two of the resistors are
shorted. | d. | There is no trouble; these voltages are
normal. |
|
|
|
31.
|
If 12 V and 17 V sources are
wired in series aiding, what is the total supply voltage?
|
|
|
32.
|
Two 100 kÙ resistors are wired in series across a 20 V source. How much voltage does each
resistor drop?
a. | 10 V | c. | 20 V | b. | 100 kÙ | d. | 100 mA |
|
|
|
33.
|
A 22 kÙ and 12 kÙ resistor are connected across a 68 V source.
How is the voltage divided?
a. | 68 V and 68
V | c. | 34 V and 34
V | b. | 22 V and 12
V | d. | 44 V and 24
V |
|
|
|
34.
|
A 500 kÙ potentiometer is connected across a 5 V source. If the voltage from the wiper to the
lower end of the potentiometer is 1.2 V, what is the resistance of that lower
part?
a. | 500
kÙ | c. | 380
kÙ | b. | 0 Ù | d. | 120
kÙ |
|
|
|
35.
|
-1.2 V, +5 V and +6 V batteries
are connected in series. The total voltage is ________.
a. | 9.8 V | c. | 1.3 V | b. | 1.2 V | d. | 12.2 V |
|
|
|
36.
|
If a 100 Ù, 220 Ù, and 330 Ù
resistor are connected in series, total resistance equals ________.
a. | 1650
Ù | c. | 650
Ù | b. | the average of the three values | d. | less than 100 Ù |
|
|
|
37.
|
If a 68 Ù, 33 Ù, 100 Ù and 47
Ù resistor are connected in series across a 9 V battery, the current
equals ________.
a. | 22.3 mA | c. | 327 mA | b. | 27.6 A | d. | 36.3 mA |
|
|
|
38.
|
If each of the six resistors in
a series circuit drops 5 V, the source voltage ________.
a. | equals 30
V | c. | depends on the
current | b. | depends on the resistor values | d. | equals 5 V |
|
|
|
39.
|
If a 4.7 kÙ, 5.6 kÙ and 10 kÙ
resistor are in series, which resistor drops the most voltage?
a. | the 4.7 kÙ resistor | b. | the 10 kÙ resistor | c. | the 5.6 kÙ
resistor | d. | That can't be determined from the given
information. |
|
|
|
40.
|
If five equal resistors
dissipate a total of 10 W in a series circuit, how much power does each resistor
dissipate?
|
|
|
41.
|
If 18 V and 6 V sources are
connected in series opposing, what is the total voltage?
|
|
|
42.
|
If three 2.2
kÙ resistors are connected in series across a 50 V source, PT equals
________.
a. | 52.08
mW | c. | 402
mW | b. | 104.2
mW | d. | 379 mW |
|
|
|
43.
|
Three resistors are connected
in series across a 60 V source. If VR1 = 19 V and VR2 = 14.3 V, then what is the voltage drop across
R3?
a. | 45.7 V | c. | 19 V | b. | 14.3 V | d. | 26.7 V |
|
|
|
44.
|
If 5 V and 16 V power supplies
are connected in series aiding, what is the total voltage?
|
|
|
45.
|
Two resistors are in series
across a 12 V source. If each resistor equals 470 kÙ, what is the
voltage across each resistor?
|
|
|
46.
|
If a 10 kÙ and 5 kÙ resistor are connected in series across a 12
V source, the voltage across the 10 kÙ resistor is ________ and the
voltage across the 5 kÙ resistor is ________.
a. | 8 V, 8
V | c. | 4 V, 8
V | b. | 8 V, 4
V | d. | 4 V, 4 V |
|
|
|
47.
|
Four series resistors are
connected across a 30 V source and carry 0.125 mA. If R1 = 10 kÙ, R2
= 33 kÙ and R3 = 47 kÙ, what is the
value of R4?
a. | 15
kÙ | c. | 1.5
kÙ | b. | 150 Ù | d. | 150
kÙ |
|
|
|
48.
|
The voltage drop across any
resistor or combination of resistors in a series circuit equals:
a. | the applied voltage across the
resistor (A). | b. | the product of the circuit current times the resistance
value. | c. | the ratio of the resistance values to the total resistance times the source
voltage. | d. | all of these. |
|
|
|
49.
|
A 50 kÙ potentiometer is connected across a 15 V source. If the voltage from the wiper to the
lower end of the potentiometer is 3.2 V, what is the resistance of that lower
part?
a. | 39.3
kÙ | c. | 0
Ù | b. | 10.7 kÙ | d. | 50
kÙ |
|
|
|
50.
|
One of the most popular
applications of a potentiometer is as an adjustable voltage divider also known as
a:
a. | voltage
control. | c. | current
control. | b. | volume control. | d. | divider control. |
|
|
|
51.
|
In a series circuit, total
power PT is calculated as:
a. | P1 × P2 × P3 ×
etc. | c. | P1 + P2 + P3 +
etc. | b. | P1 ÷ P2 ÷ P3 ÷ etc. | d. | 1/P1 + 1/P2 + 1/P3 + etc. |
|
|
|
52.
|
In a series circuit, the
largest amount of power is dissipated by:
a. | the largest
resistor. | b. | the first resistor. | c. | the smallest resistor. | d. | any resistor, since the current is the same throughout the
circuit. |
|
|
|
53.
|
An open in a series circuit
results in:
a. | no current
flow. | b. | source voltage appearing across the open. | c. | no power dissipation. | d. | all of
these. |
|
|
|
54.
|
A short in a series circuit
results in:
a. | decreased or reduced current
flow. | c. | increased circuit
resistance. | b. | decreased power consumption. | d. | increased or maximum current
flow. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Refer to Figure 4-2a. Voltage B
to ground is less than normal. What could be the cause of failure?
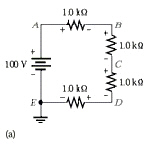
Figure 4-2a
a. | short between E and
D | c. | open between C and
D | b. | open between B and
C | d. | short between A and
B |
|
|
|
56.
|
Refer to Figure 4-2a. Voltage
from C to ground is 100 V. What is the probable cause of failure?
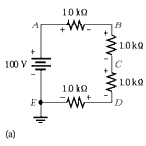
Figure 4-2a
a. | short between A and
B | c. | open between A and
B | b. | open between E and
D | d. | voltage reading is
normal |
|
|
|
57.
|
Refer to Figure 4-2a. The
resistor between points E and D looks charred. What most likely would cause
this?
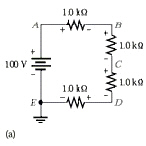
Figure
4-2a
a. | open A and the power
supply | c. | short between A and
B | b. | short between A and
D | d. | Any of these could cause this
problem. |
|
|
|
58.
|
What type of resistor could be
used as variable voltage-divider?
a. | rheostat | c. | thermistor | b. | potentiometer | d. | any one of the above |
|
|
|
59.
|
What is the easiest, most
practical measurement performed during troubleshooting?
a. | power | c. | voltage | b. | resistance | d. | current |
|