Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
1.
|
An atom is the smallest particle of an ________ that retains the characteristics
of that element.
|
|
|
2.
|
The nucleus consists of positively charged particles call protons and uncharged
particles call ____________.
|
|
|
3.
|
The basic particles of negative charge are called ________.
|
|
|
4.
|
All elements are arranged in the periodic table of elements in order according
to their atomic ___________.
|
|
|
5.
|
Electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom at certain distances from the
__________.
|
|
|
6.
|
In an atom, the orbits are grouped into energy _______ known as shells.
|
|
|
7.
|
The outermost shell is known as the _______ shell, electrons in this shell are
called valence electrons.
|
|
|
8.
|
If an electron absorbs a photon of sufficient energy, it escapes from the atom
and becomes a ______ electron.
|
|
|
9.
|
Any time an atom or group of atoms is left with a net charge, it is called an
______.
|
|
|
10.
|
_________ is the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.
|
|
|
11.
|
Electrical charge is an electrical property of matter that exists because of an
excess or _________ of electrons.
|
|
|
12.
|
Materials with charges of opposite polarity are attracted to each other;
materials with charges of the same polarity are _________.
|
|
|
13.
|
Electrical charge is measured in ___________.
|
|
|
14.
|
A voltage source provides electrical energy or ____________ force (emf), more
commonly known as voltage.
|
|
|
15.
|
A ___________ is a type of voltage source that is composed of one or more cells
that convert chemical energy directly into _________ energy.
|
|
|
16.
|
In a battery, the terminal that supplies electrons has a surplus of electrons
and is the negative electrode or _______.
|
|
|
17.
|
The electrode that acquires electrons has a positive potential and is the
___________.
|
|
|
18.
|
Although the voltage of a battery cell is fixed by its chemestry, the capacity
is variable and depends on the ________ of materials in the cell.
|
|
|
19.
|
A fuel cell is a device that converts electrochemical energy into dc ________
directly.
|
|
|
20.
|
The operation of solar cells is based on the photovoltaic effect, which is the
process whereby light energy is converted directly into _________ energy.
|
|
|
21.
|
Electrical Generators convert ___________ energy into electrical energy using a
principle called electromagnetic induction.
|
|
|
22.
|
The thermocouple is a thermoelectric type of voltage source that is commonly
used to sense ______________.
|
|
|
23.
|
Electrical __________ is the rate of flow of charge.
|
|
|
24.
|
Current is measured in a unit called the ________ or amp for short, symbolized
by A.
|
|
|
25.
|
Resistance is the __________ to current.
|
|
|
26.
|
The reciprical of resistance is ____________, symbolized by G.
|
|
|
27.
|
The unit of conductance is the ________, symbolized by S.
|
|
|
28.
|
Components that are specifically designed to have a certain amount of
resistances are called ______________.
|
|
|
29.
|
An electric circuit consists of a voltage source, a load, and a ______ for
current between the sourse and the load.
|
|
|
30.
|
The load is a device on which work is done by the _______ through it.
|
|
|
31.
|
An electric circuit can be represented by a schematic, a diagram that shows the
interconnection of components, using standard _______ for each element.
|
|
|
32.
|
Switches are commonly used for ___________ the opening or closing of
circuits.
|
|
|
33.
|
_______ are the most common form of conductive material used in electrical
applications.
|
|
|
34.
|
__________ is the reference point in an electric circuit.
|
|
|
35.
|
A DMM is a multifunction electronic instrument than can measure voltage,
current, or ____________.
|
|
|
36.
|
The _______ is a device on which work is done by the current through it.
|
|
|
37.
|
An electric circuit can be represented by a ____________.
|
|
|
38.
|
____________ are commonly used for controlling the opening and closing of
circuits.
|
|
|
39.
|
This symbol is for a _______ switch. (USE THE ABBRIVIATE IN CAPS FOR YOUR
ANSWER) 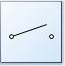
|
|
|
40.
|
This symbol is for a _______ switch. (USE THE ABBRIVIATE IN CAPS FOR YOUR
ANSWER) 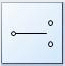
|
|
|
41.
|
This symbol is for a _______ switch. (USE THE ABBRIVIATE IN CAPS FOR YOUR
ANSWER) 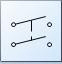
|
|
|
42.
|
This symbol is for a _______ switch. (USE THE ABBRIVIATE IN CAPS FOR YOUR
ANSWER) 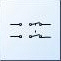
|
|
|
43.
|
The basic difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker is that when a fuse is
“blown” it must be replaced; but when a circuit breaker opens, it can be ________ and
reused repeatedly.
|
|
|
44.
|
_________ is the reference point in an electric circuit.
|
|
|
45.
|
A DMM is a ____________ electronic instrument that can measure voltage, current,
or resistance.
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | Semiconductors | c. | Insulators | b. | Conductors |
|
|
|
46.
|
Nonmetallic materials that are poor conductors of electric current.
|
|
|
47.
|
Classified below conductors in their ability to carry current because they have
fewer free electrons than do conductors.
|
|
|
48.
|
Materials that readily allow current.
|
|
|
Different types of Batteries a. | Lithium-ion | e. | Lead-Acid | b. | Nickel-metal hydride | f. | Silver Oxide | c. | Zinc-Air | g. | Alkaline | d. | Carbon-zinc | h. | Lithium-MnO2 |
|
|
|
49.
|
Used in palm-type computers, photographic equipment, toys, radios.
|
|
|
50.
|
Used in flashlights, know as AAA, AA, C and D.
|
|
|
51.
|
Used in smoke alarms, memory backup and communications equipment.
|
|
|
52.
|
Used in Medical monitoring instruments and other frequency-use
applications
|
|
|
53.
|
Used in laptops and cell phones.
|
|
|
54.
|
Used in watches and hearing aids.
|
|
|
55.
|
Used in defense and aerospace.
|
|
|
56.
|
Rechargable battery used in automotive, marine, and other similar
appliances.
|