Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution.
Find the
distance traveled in 16 seconds by an object traveling at a constant velocity of 20 feet per
second.
a. | calculus, 320 ft | b. | calculus, 340 ft | c. | precalculus, 320
ft | d. | calculus, 640 ft | e. | precalculus, 640
ft |
|
|
|
2.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. Find the
distance traveled in 20 seconds by an object moving with a velocity of 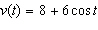
feet per second. a. | calculus, 162.4485 ft | b. | precalculus, 163.7985 ft | c. | calculus, 165.4777
ft | d. | precalculus, 165.4777 ft | e. | precalculus, 162.4485
ft |
|
|
|
3.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. A cyclist
is riding on a path whose elevation is modeled by the function 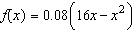 where
x and 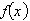 are measured in miles. Find the rate of
change of elevation when x = 4. 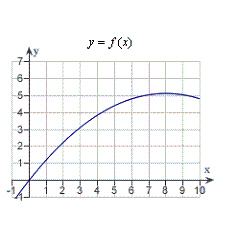 a. | precalculus, 0.08 | b. | calculus, 0.2 | c. | calculus,
0.64 | d. | calculus, 0.08 | e. | precalculus,
0.2 |
|
|
|
4.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. A cyclist
is riding on a path whose elevation is modeled by the function 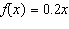 where
x and 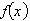 are measured in miles. Find the rate of
change of elevation when x = 5. 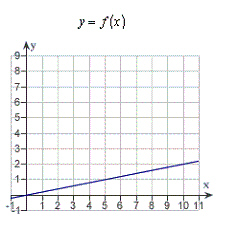 a. | calculus, 2 | b. | precalculus, 0.2 | c. | calculus,
0.2 | d. | precalculus, 2 | e. | precalculus,
0.45 |
|
|
|
5.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. Find the
area of the shaded region bounded by the triangle with vertices (0,0), (8,9), (17,0). 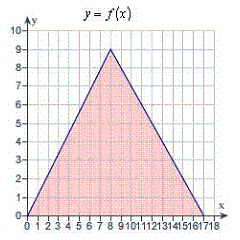 a. | precalculus , 153 | b. | calculus , 229.5 | c. | precalculus ,
76.5 | d. | precalculus , 229.5 | e. | calculus , 153 |
|
|
|
6.
|
Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether
calculus is required. If the problem can be solved using precalculus, solve it. If the problem seems
to require calculus, use a graphical or numerical approach to estimate the solution. Find the
area of the shaded region. 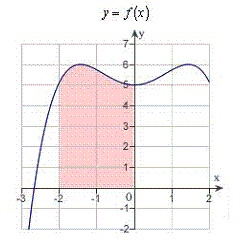 a. | calculus , 11 | b. | precalculus , 11 | c. | precalculus ,
13 | d. | calculus , 16 | e. | precalculus ,
16 |
|
|
|
7.
|
Consider the function 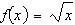 and the point 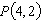 on the graph of f. Graph f and the secant line passing through 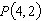 and 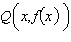 for 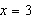 .
|
|
|
8.
|
Consider the function 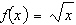 and the point 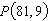 on the graph of f. Find the slope of the secant line passing through 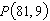 and 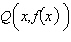 for 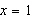 . Round your
answer to four decimal places. a. | m=0.1000 | b. | m=0.0122 | c. | m=0.0122 | d. | m=0.3133 | e. | m=0.1000 |
|
|
|
9.
|
Consider the function 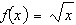 and the point P(64,8)
on the graph of f. Consider the secant lines passing through P(64,8) and
Q( x, f( x)) for x values of 61, 63, and 65. Find the slope of each secant
line to four decimal places. (Think about how you could use your results to estimate the slope
of the tangent line of f at P(64,8), and how to improve your approximation of the
slope.) a. | 0.0633 , –0.0627 , 0.0623 | b. | 0.0633 , 0.0627 , 0.0623 | c. | 0.0317 , 0.0314 ,
0.0312 | d. | 0.0633 , –0.0627 , –0.0623 | e. | –0.0317 , –0.0314 ,
–0.0312 |
|
|
|
10.
|
Consider the function 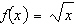 and the point 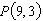 on the graph of f. Estimate the slope m of the tangent line of f at
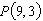 . Round your answer to four decimal places.
a. | m=0.1667 | b. | m=0.0832 | c. | m=0.3800 | d. | m=0.0556 | e. | m=0.0833 |
|
|
|
11.
|
Consider the function 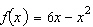 and the point 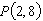 on the graph of f. Graph f and the secant line passing through 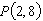 and 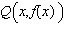 for 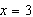 .
|
|
|
12.
|
Consider the function 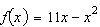 and the point 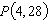 on the graph of f. Find the slope of the secant line passing through 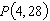 and 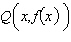 for 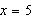 . Round your
answer to one decimal place. a. | 3.5 | b. | 2.0 | c. | 3.0 | d. | 4.5 | e. | 9.0 |
|
|
|
13.
|
Consider the function 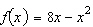 and the point 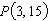 on the graph of f. Estimate the slope of the tangent line of f at 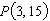 .
|
|
|
14.
|
Use the rectangles in the graph given below to approximate the area of the
region bounded by 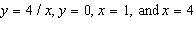 Round your answer to three decimal
places. 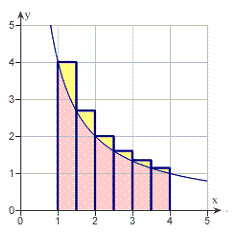 a. | 2.481 units2 | b. | 6.371 units2 | c. | 3.585
units2 | d. | 6.872 units2 | e. | 6.903
units2 |
|
|
|
15.
|
Consider the length of the graph of 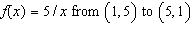 Approximate the length of
the curve by finding the sum of the lengths of four line segments, as shown in following figure.
Round your answer to two decimal places. 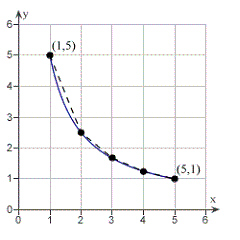 a. | 6.11 | b. | 8.12 | c. | 5.66 | d. | 8.49 | e. | 7.11 |
|