True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
The number of equations must equal the number of unknowns in a circuit.
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
2.
|
When basic circuit elements are interconnected to form a circuit, the resulting
interconnection is described in terms of nodes, paths, branches, ________, and meshes.
|
|
|
3.
|
The number of unknown currents in a circuit equals the number of _______, b,
where the current is not known.
|
|
|
4.
|
The first step is to make a neat layout of the circuit so that no branches cross
over and to mark clearly the __________ nodes on the circuit diagram.
|
|
|
5.
|
A node voltage is defined as the voltage rise from the reference node to a
_____________ node.
|
|
|
6.
|
When a voltage source is the only element between two essential _______, the
node-voltage method is simplified.
|
|
|
7.
|
In general, when you use the node-voltage method to solve circuits that have
voltage sources connected directly between essential nodes, the number of unknown node voltages is
_______.
|
|
|
8.
|
When a voltage source is between two essential nodes, we can combine those nodes
to form a _____________.
|
|
|
9.
|
A ___________ current is the current that exists only in the perimeter of a
mesh.
|
|
|
10.
|
If the circuit contains dependent sources, the mesh-current equations must be
supplemented by the appropriate _________ equations.
|
|
|
11.
|
When a branch circuit includes a current source, the mesh-current method
requires some ___________ manipulations.
|
|
|
12.
|
To create a _____________, we mentally remove the current source from the
circuit by simply avoiding this branch when writing the mesh-current equations.
|
|
|
13.
|
The greatest advantage of both the node-voltage and mesh-current methods is that
they reduce the number of simultaneous ___________ that must be manipulated.
|
|
|
14.
|
A ________ transformation allowes a voltage source in a series with a resistor
to be replaced by a current source in parallel with the same resistor or vice versa.
|
|
|
15.
|
Thevenin and Norton __________ are circuit simplification techniques that focus
on terminal behavior and thus are extremely valuable aids in analysis.
|
|
|
16.
|
To find the Thevenin equivalent of a circuit, we first calculate the
open-circuit ________ of 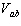 .
|
|
|
17.
|
The next step is to place a short circuit across the terminals and calculate the
resulting short-circuit ___________.
|
|
|
18.
|
A Norton equivalent circuit consists of an independent current source in
parallel with the Norton equivalent _________.
|
|
|
19.
|
Circuit analysis plays an inportant role in the analysis of systems designed to
transfer _______ from a source to a load.
|
|
|
20.
|
Thus maximum power transfer occurs when the _________ resistance 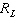 equals the Thevenin resistance 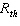 .
|
|
|
21.
|
A linear system obeys the principle of superposition, which states that whenever
a linear system is excited, or driven, by more than one independent source of energy, the total
response is the _____ of the individual responses.
|
|
|
22.
|
When applying superposition to linear circuits containing both independent and
dependent sources, you must recognize that the dependant sources are never _________.
|
Matching
|
|
|
a. | planar circuit | e. | mesh | b. | branch | f. | path | c. | essential
node | g. | node | d. | loop | h. | essential
branch |
|
|
|
23.
|
A point where two or more circuit elements join.
|
|
|
24.
|
A node where three or more circuit elements join.
|
|
|
25.
|
A trace of adjoining basic elements with no elements included more than
once.
|
|
|
26.
|
A path that connects two nodes.
|
|
|
27.
|
A path which connects two essential nodes without passing through an essential
node.
|
|
|
28.
|
A path whos last node is the same as the starting node.
|
|
|
29.
|
A loop that does not enclose any other loops.
|
|
|
30.
|
A circuit that can be drawn on a plane with no crossing branches.
|